はじめにと重要性
マンゴー(Mangifera indica L Family Anacardiaceae)は、パキスタンで2番目に主要な果実作物です。現在、それは93.42千ヘクタールの面積で栽培されており、生産量は915.7千トンです。マンゴーの作付面積は増加していますが、生産量の増加は比較的遅いです。パンジャブ州の主なマンゴー栽培地区はムルタンです。 バハーワルプル、 ムザファルガルとラヒムヤルカーン。シンド州では、主にミールプルハースで栽培されています。 NWFP州のハイデラバードとタッタはペシャワールとマルダンで栽培されています。シンドの気候は、州に初期の種類のマンゴーを栽培する特権を与えたパンジャブよりも約1か月早く暖かくなります。続いて、 パンジャブ州で後期品種が成長するという新しい傾向が広く普及し、市場期間が延長され、輸出可能な余剰が増えました。

このおいしい果物は栄養的に優れています、 いくつかのビタミンとミネラルの供給源。パキスタンは5.86%の世界のマンゴーを生産しており、3番目に大きな生産国です。その輸出は進んでおり、かなりの外国為替収益をもたらしています。中東を含むマンゴーの輸出も、英国や他のヨーロッパ市場への道を見つけました。適切な推進力とドイツへの輸出拡大を考えると、需要は50%にまで上昇すると考えられています。 日本中国と香港。
気候と土壌
マンゴー栽培に適した生態学的条件は次のとおりです。
- 標高は200メートルから300メートルの範囲です。
- 適切な温度範囲は15〜40oCです。低温は非常に有害です。霜や熱風は木に大きなダメージを与えます。若い植物は霜や熱風から保護する必要があります。
- 高温多湿の気候が適しています。降雨量の多い地域では、 果物の品質が影響を受ける可能性があります。
- マンゴーはさまざまな土壌で育つことができますが、水はけがよく、 深く肥沃な土壌が最適です。塩害を受けた土壌は、その栽培には適していません。
伝搬:
- 繁殖は、地元の苗木に接ぎ木するさまざまな手段によって行われます。
- 移植に適した苗床の年齢1。5〜2。0年
- 移植の時間:
- 春:2月/ 3月
- 秋:9月/ 10月
- ベアリングの開始までの時間:4-5年
- フルベアリングまでの時間:6〜7年
- 通常の経済的ベアリング寿命:30-50年
- 開花時期:2月/ 3月
主要な商用品種:
- シンド:シンド、 Gulabkhas、 スワルナリス、 バガンパリ、 コレクタ、 ニーラム
- パンジャブ:マルダ、 ラングラ、 アマン・ドゥセリ、 アンワルラトール、 Samer Bahisht、 ファジリカランとセンセーション。
- NWFP:LengraとSamer Bahisht
- バルチスタン:シンドリとバンガンパリ
生産技術:
- 年間作物水需要:500-750 mm
- 灌漑間隔:
- 若い植物:7日
- 冬の成熟した木:15-20日
- 夏の成熟した木:8-10日
- 若い植物あたり10〜30 kg、完全に成長した木あたり80〜100kgの割合で農場の肥料を適用します。
- 3〜4 kgのSSPを適用し、 開花前(12月から1月)に2〜3kgの硫酸カリウムと2〜3kgの尿素。
- 2つの等しい用量(3月/ 4月)で結実した後、さらに2〜3kgの尿素を適用します。
剪定
マンゴーは通常、主幹を覆う優雅なドーム型を想定しています。ただし、剪定は行われません。 毎年、果物の収穫が病気になった後、 乾燥、 壊れた枝や地面に触れているものは剪定する必要があります。 3〜4年ごとに果樹園を活性化するには、古い木材の15〜20%を取り除くことをお勧めします。
収穫
果実が完全に発達して成熟したときに、摘み取りを行う必要があります。果実の自然な落下は、果実が摘み取られる準備ができていることの主な兆候です。さまざまな地域のさまざまな品種がさまざまな時期に熟します。シンドでは、 マンゴーの品種は5月から6月に熟し始めます。パンジャブ州では、成熟は6月から始まり、8月中旬まで続きます。 NWFPでは、 収穫は遅くなり、マンゴーが利用できる期間を延長するのに役立ちます。期待される収量は、1本の木あたり40〜100kgです。
マンゴーの病気:
うどんこ病
花序に症状が見られますが、 花序の茎、 葉と若い果実。病気の特徴的な症状は、これらの部分の真菌の白い表面的な粉状の成長です。効果的な花は時期尚早に落ちる可能性があり、若い果実は大理石のサイズに達するまで木に残り、その後時期尚早に落ちる可能性があります。未受精の感染した花や若い果実を落とすと、深刻な作物の損失につながります(20-80%)。
コントロール:-
- 病気の葉と奇形の円錐花序の剪定は、一次接種を減らします。
- 開花期に全身殺菌剤を3回スプレーすることを12〜15日間隔で行うことをお勧めします。
- 花が25%開いている場合は、1回目のスプレーをお勧めします。
炭疽病/ブロッサムブライト
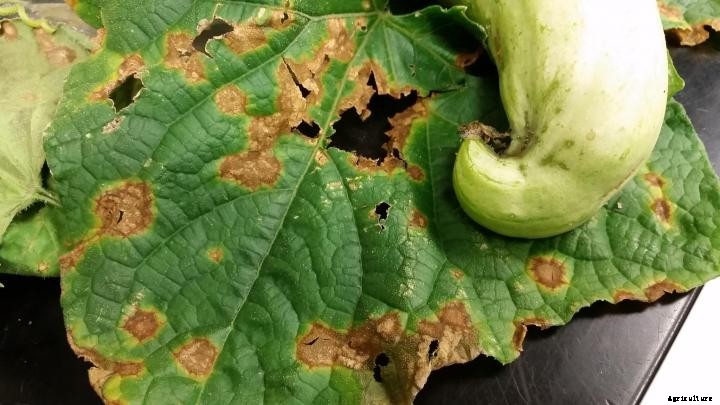

炭疽病はマンゴーの木のさまざまな部分に現れます。花序について、 この病気の最も初期の症状は、花柄や花に黒褐色の斑点ができることです。穂と開花に小さな黒い斑点が現れ、 徐々に拡大し、花を死に至らしめます。感染した花が落ちる、 花柄により多くの持続性スパイクを残し、 これは深刻な作物の損失につながります(10-90%)。95-97%R.H。窒素が過剰です。
コントロール:-
- 病気の葉、 フラワーズ、 果樹園の床に横たわっている小枝や果物を集め、木から感染した小枝をすべて剪定して燃やす必要があります。
- 花の感染は、春のシーズン中に12〜15日間隔で2〜3回の接触または全身殺菌剤のスプレーによって効果的に制御できます。
マンゴー奇形

奇形はパキスタンのマンゴー栽培地域にとって深刻な脅威であり、最大70%の作物の損失を引き起こします。最近の発見は、この病気が真菌起源である可能性があることを示しています。労働者によって説明された2つの異なるタイプの症状は、栄養奇形(MV)と花奇形(MF)です。栄養奇形は、接ぎ木された植物よりも若い実生と実生の木でより顕著です。影響を受けた実生は過剰な栄養枝を発達させました、 成長が限られている、 腫れ、非常に短い節間があります。
花序の奇形(MF)は花序の病気です。 (MF)の最も特徴的な症状は、節間の縮小と緻密化であり、奇形にほうきのような外観を与えます。感染した移植材料と傷
コントロール :-
現在のところ、 マンゴー奇形に対する明確な管理措置を提唱することはできません。ただし、以下は奇形の発生率を減らす可能性があります
- 繁殖のために奇形の花序を持つ木からの穂木を避けることをお勧めします。
- 繁殖には、認定された苗木のみを使用する必要があります。
- 病気の症状がよく表現されるとすぐに、 影響を受けた端末は、隣接する15〜20cmの明らかに健康な部分と一緒に剪定し、焼却する必要があります。
葉の病気:

マンゴー植物は多かれ少なかれ以下に述べる様々な葉の病気にかかりやすいですが、最も重要なものは詳細に議論されています:
- 炭疽病
- かさぶた
- フォーマ枯れ
- 灰色の枯れ
- アルテルナリアリーフスポット
- 細菌性潰瘍
炭疽病
特徴的な症状は、葉の表面全体に散在するさまざまなサイズの楕円形または不規則な茶色から濃い茶色の斑点として現れます。湿気の多い条件下では、 真菌は急速に成長します。若い葉は古い葉よりも引き付けやすいです。昆虫の攻撃は病原体の侵入を促進し、病気の発生率を高める可能性があります。
コントロール:-
葉の感染は、春とモンスーンの季節の後に銅ベースの殺菌剤のスプレーによって制御することができます。
アルテルナリアリーフスポット

症状は最初は小さく見えますが、 葉の表面に茶色がかった円形の斑点。後で、 高濃度の茶色の黒い斑点が葉の薄層全体に均一に発生します。症状は葉の下側でより顕著です。柔らかい葉は成熟した葉よりも感受性が高いことがわかっています。
コントロール:-
この病気は、銅ベースの殺菌剤を含む定期的な野外散布プログラムによって防除することができます。
細菌性潰瘍(Xanthomonas mangiferae)
葉の上で、 不規則な隆起した病変から角張った隆起した病変に浸した微細な水は、通常、頂点に密集しています。若い葉では、ハローは大きくてはっきりしています、 古い葉の上にいる間、 それらは狭く、光に対してのみ観察することができました。重度の感染症では、 葉が黄色に変わり、落ちます。25-300C&> 90%R.H。雨天
コントロール:-
果樹園の定期検査、 病気の予防策として、衛生と苗の認証が推奨されます。
銅ベースの殺菌剤のスプレーは、細菌性潰瘍を制御するのに効果的であることがわかっています。
果物の病気/収穫後の病気
炭疽病
この病気は若い果物や輸送中や保管中によく見られます。収穫前の段階での潜伏感染は、収穫後の腐敗の原因です。ストレージでは、 黒い斑点が生成されます。最初は斑点は丸いですが、後で果実全体に大きな不規則な斑点を形成します。斑点には大きな深い亀裂があり、真菌は果実の奥深くまで浸透して広範囲の腐敗を引き起こします。
コントロール:-
収穫前の感染は、激しいシャワーの完了後に銅ベースの殺菌剤を噴霧することによって管理できます。
収穫後の感染は、潜在性感染を減らすための収穫前のスプレーとして管理でき、収穫後の果実の熱水/殺菌剤による処理により、残った潜在性感染を根絶することができます。
茎端腐敗

成熟中の果実は、通常、茎の端で突然茶色から黒色になります。 2〜3日以内に果実全体が黒くなり、病気が下向きに進行します。 したがって、果物の面積の半分が含まれます。果実全体のフラッシュはしばしばしわも観察されますが。影響を受けた皮膚はしっかりしたままですが、腐敗が下の歯髄に入り込み、不快な臭いを発します。
コントロール:-
- 果物の迅速かつ適切な取り扱いは、病気の発生を最小限に抑えることができます。
- 果実は10mmの茎で収穫する必要があります。
- 全身殺菌剤または銅ベースの殺菌剤の収穫前スプレーは、SERの発生を減らします。
- 収穫後、カルベンダジムまたはチオファネートメチル(0.05%)を添加したお湯に52±1oCで15分間果実を浸すと、病気が防除されます。
衰退障害
衰退は一般的な用語であり、マンゴー植物は、通常、生物的および非生物的ストレスに関連するさまざまな衰退障害の影響を受けます。
-
- 死ぬ
- 小枝の枯れ
- 樹脂病
- 樹皮の分裂
- 樹皮のスケーリング
- しおれ
- マンゴー突然死症候群(MSDS)
重要なマンゴー衰退障害を以下に説明します。
死ぬ
この病気は一年中目立ちますが、10月と11月に最も目立ちます。これは、特に古い木で小枝を上から下に乾燥させた後、葉を乾燥させて火の焼け焦げのように見えることを特徴としています。上葉は色を失い、徐々に乾きます。葉全体の乾燥は、縁の上方への転がりを伴います。そのような葉は縮む、 しわが寄った小枝をすべて裸のままにして、1か月以内に落ちます。 これは、病気の進行段階の特徴的な症状です。
干ばつ、 激しい痛み、 高温、 弱い木、 サンスコーチ、 高湿度、 栄養不足と身体的損傷。
コントロール:-
- 影響を受けた小枝(感染部位の3フィート下)を剪定した後、銅ベースの殺菌剤を噴霧することが、病気を防除するための最も効果的な方法です。
- 重症の場合、 病気にかかった木の天蓋の下の深さ9インチまでの土壌を取り除き、運河のシルトを補充することによる土壌改良、 化学肥料とFYMの推奨用量と、影響を受けた小枝の剪定、それに続く15日間隔での銅ベースの殺菌剤の3回の連続スプレーも推奨されます。
小枝の枯れ
病気は小枝に細長い黒い壊死領域を作ります。葉は上に向かってゆっくりと垂れ下がり、最終的には落ちます。非常に若い枝は、先端から下に向かって乾燥し始めます。怪我、 昆虫の攻撃、 高温の弱い植物、 水ストレス、 霜と物理的損傷。
コントロール:-
果樹園の床に横たわっている病気の小枝を集め、木から感染した小枝をすべて剪定して燃やす必要があります。
銅ベースの殺菌剤の葉面散布は、良好な防除を反映しています。
樹脂病

若いマンゴーの木の約30〜40%は、特にマンゴーの木が砂質土壌に植えられたときに樹脂病の影響を受けますが、その蔓延は他のマンゴー栽培土壌でも見られます。この病気は、影響を受けた木材の表面にガムが大量ににじみ出るのが特徴です。 幹の樹皮や大きな枝にもありますが、亀裂の枝によく見られます。重症の場合、 歯茎の小滴が茎に滴り落ち、樹皮が暗褐色に変わり、縦方向の亀裂が生じます。
コントロール:-
- この病気は、銅ベースの殺菌剤を定期的にスプレーすることで防除できます。
- 病気の樹皮/部分を取り除く必要があります、 洗浄し、銅ベースの殺菌剤ペーストで覆った。
- 木の幹の周りの砂質土壌に硫酸銅500gを適用することも提唱されています。
吠え声が割れる
樹皮のひび割れは、深い縦方向のひび割れの発生を特徴としています。発根は亀裂とは関係ありませんが、下にある木材はひどく穴が開いています。歯茎のポケットもひび割れとともに目立ちます。その後、樹皮が乾燥して剥がれ、剥皮効果が生じます。 葉の黄変と脱落、それに続く枝のダイバック。
コントロール:-
- オキシ塩化銅の噴霧。
- 硫酸銅の土壌施用。
- 枯れた樹皮の除去とボルドーペーストの貼り付け。
根腐れ

感染は、地面レベルまたはその下で、円形から不規則な水に浸したパッチで発生します。これらのパッチは拡大し、最終的には茎の基部全体をガードルで囲みます。腐敗のため、 患部組織が柔らかくなり、 ダークブラウンまたはブラック。
コントロール:-
チオファネートメチルによる土壌処理、 カルベンダジムまたはオキシ塩化銅@ 2g / ft2をお勧めします。
成長期間中、銅ベースの殺菌剤を植物に噴霧する必要があります。
マンゴー突然死症候群

マンゴー突然死症候群(MSDS)は、1997年以来、パキスタンで重要な病気になっています。これは、おそらくLasiodiplodiatheobromaeのようなBotryosphaericaceous菌と協調してCeratocystisfimbriataによる感染と密接に関連しています。不適切な灌漑と根の損傷は、この病気の主要な素因として発見されています。影響を受けたマンゴーの木にはしおれの症状があります。潰瘍は血管の変色の領域に発生する可能性があり、潰瘍は茎からガムを滲出させます。しおれた葉は通常、乾燥してかなり突然カールしますが、数週間は木に付着したままになります。それは深刻な病気であり、日ごとに悪化し、明らかに健康に見えるマンゴー植物が数日以内に死に、パキスタンの貴重な富を破壊しています。これまで、パキスタンのさまざまなマンゴー栽培地域で4〜12%の死亡率が観察されています。
コントロール :-
この病気を適切に管理するには、早期発見が非常に重要です。この目的のために、科学者はこの症候群を集合的な知恵で5つのカテゴリー(0-5段階)に分けました。 ASLPプロジェクトの下でのマンゴー栽培者のガイドラインのために、各段階の詳細な図解が作成されました。ただし、ここではいくつかの重要な点について説明しています。
- 0段階=無病
- 1および2段階=疾患の重症度が50%未満
- 3および4段階=50%を超える疾患重症度
- 5段階=枯れた植物と完全にしおれた植物
3を示す植物を根こそぎにします。 すぐに4&5段階で、殺菌剤で土壌を処理します。この地域の土壌ソラリゼーションも推奨されます。
次の方法で1と2段階に落ちる植物を扱います:
- 感染部分を引っ掻いた後、チオファネートメチルまたはカルベンダジムを250kg /リットルで1週間間隔で3回貼り付けます
- これらの殺菌剤は、5g / 20ml /穴で同じ間隔で3回注入され、直径½インチの樹木の主幹に4つの穴が形成されます。 45oCで4-6インチの深さ。これらの穴は、地面から始まり、周囲全体をカバーする1フィートの高さに作成する必要があります。 FYMリンの適用を通じて、病気にかかった植物の土壌条件を最適化し、 カリと石膏(必要な場合)。
- 開花を解除することにより、植物の要件を最小限に抑えます。 果物のタイミング、 微量栄養素の剪定と葉面散布。
- 以下の推奨事項は、病気を示さない(0段階)植物に対して与えられます。
- 必要なときはいつでも適切な灌漑を行ってください。
- 「ワット」または傾斜を作ることにより、水を茎から3〜4フィート離してください。
- キャノピーの下の領域はフィールドレベルである必要があります。
- マンゴー果樹園での間作は避けてください。
- キクイムシとシロアリの蔓延を適切に管理します。
- 肥料の施用については、部門の推奨事項に従ってください。
- 有機物は、できれば毎年、FYMまたは緑肥の形で追加する必要があります。
- マンゴー果樹園での鋤や耕作は常に避けてください。
- チオファネートメチルまたはカルベンダジム@ 2g /リットルのスプレーは、スプレースケジュールに含める必要があり、樹木の全領域を地面までカバーする方法で行う必要があります。
- 予防策として健康な植物にこれらの殺菌剤を注射することも提唱されています。
- MSDS以外のあらゆるタイプの衰退障害を示す植物は、それに応じて治療することができます。
マンゴーの害虫:

ホッパー
症状:
くさび形のニンフと成虫は、柔らかい部分の樹液に穴を開けて吸います。 植物の活力を低下させ、特に花序を破壊し、果実の落下を引き起こします。樹液の激しい穿刺と継続的な排出は、感染した組織のカールと乾燥を引き起こします。それらはまた、甘い粘着性物質を排出することによって作物に損傷を与え、すすのカビの発生を促進します。
- 密な植栽を避け、 開いたキャノピーを維持しました。梅雨が明けたら、混雑した枝を刈り取ります。
- 果樹園は、定期的な耕作と雑草の除去によって清潔に保つ必要があります。
- 捕食者のような生物制御剤の保存、 マラダボニネンシス、 Chrysopa lacciperda、 卵寄生虫、 ポリネマ属Gonatocerussp。 Tetrastichussp。と真菌、 Verticilliumlecanii。
- ホッパー個体群の初期段階での0.2%ニンビシジンまたはアザジラクチン3000 ppm @ 2m / lの噴霧。
- ラムダシハロトリン5%EC @ 0.5mlまたはイミダクロプリド200SL @ 0.25 ml / lまたはチアメタキサム(0.05%)またはプロパノホス(0.05%)をスプレーします。ホッパーの個体数が多い場合は、穂形成の初期段階で最初の噴霧を行う必要があります。 5〜10穂以上であり、 穂の全長段階での2回目のスプレーと結実後の3回目のスプレー(エンドウ豆のサイズ)。
- 化学スプレーは最小限に抑える必要があり、必要に応じて行う必要があります。
- 害虫が野外抵抗性を発達させる傾向を打ち消すために、殺虫剤の合理的な輪作が望ましい。
コナカイガラムシ

症状:
成虫は白っぽい粉で覆われ、木の幹の樹皮の間にコロニーを形成します。 若い芽と穂。ニンフは木に登り、花序に落ち着き、花を落とします。 フルーツセットに影響を与えます。彼らはまた、蜂蜜の露を排泄します、 粘着性物質、 すすの型の開発を容易にします)。
管理
- 10月に果樹園が水で氾濫すると卵が殺されます。
- 11月の果樹園の耕作。
- 木の幹の周りの土をかき集めて、卵を天敵と太陽にさらします。 1月中に雑草を取り除き、クロルピリホスダスト1.5%@ 250g /木と混合します。
- 泥塗り後、 アルカテン(400ゲージ)による木の幹のバンディング、 25cm幅のシートはsutliの助けを借りて自由なトランクに固定する必要があります、 地上30cmで、1月の最後の週にBeauveriabassiana製品(2g /リットル1×107胞子/ ml)または5%NSKEを木の周りに散布します。
- トランク。
- 生物防除剤の保存、 白きょう病菌、 捕食者、 Menochilus sexmaculatus、 RodoliafumidaとSumniusrenardi。
- コシネリド捕食者の10〜15匹の幼虫を放出し、 木ごとのC.montrozieri。
- ニンフがツリースプレーカルボスルファン(0.05%)またはジメトエート(0.04%)で上昇した場合
花序/葉/小枝ミッジ
症状:幼虫は花序の軸を通り抜け、花序を完全に破壊します。 E.インディカによる損傷は、花序の曲がりと乾燥を引き起こします。 2回目の攻撃は、若いウジがこれらの柔らかい果実に穴をあけ、ゆっくりと黄色に変わり、最終的に落下するときに、結実から始まります。 3番目の攻撃は、花序を取り囲む柔らかい「新しい葉」に対するものです。最も有害なものは、花序全体が破壊される最初の攻撃です。花序は発育阻害を示し、その軸は曲がります、 幼虫の入り口で(図7&8)。
ミッジ管理
- 出没した穂の葉と小枝の収集と処分。
- 10月から11月に果樹園を深く耕し、蛹と休眠中の幼虫を太陽の熱にさらして殺します。
- 4月/ 5月にホワイトペーパーで幼虫の個体数を監視し、個体数に基づいてクロピリホス(1.5%)ダストを適用します。
- つぼみの破裂段階でジメトエート(0.05%)をスプレーします。
ミバエ
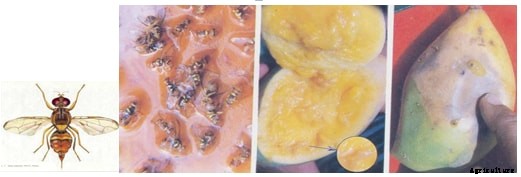
症状:雌は、先のとがった産卵管の助けを借りて成熟した果実の外壁に穴を開け、成熟した果実の中果皮の内側に小さなクラスターに卵を挿入します。孵化について、 ウジは果実の果肉を食べ、感染した果実はさらなる二次感染のために腐敗し始めます。
管理
- 収穫前(30〜40日)に、感染した果実や落ちた果実を集めて処分し、それ以上の予防を行います。 人口の増加と持ち越し。
- 11月から12月に果樹園を耕し、蛹を太陽の熱にさらして殺します。
- エタノールに浸したメチルオイゲノール木製ブロックトラップの吊り下げ、 4月から8月までの結実期間中のメチルオイゲノールとマラチオン(6:4:1)@ 10トラップ/ haは、地上3〜5フィートでしっかりと結び付けます。
- 重度の寄生の間に成虫のハエを制御するために、毒餌を置くこと、すなわちタンパク質加水分解物+マラチオン50ml + 200ml糖蜜を2リットルの水に噴霧し、さらに18リットルの水を餌毒に加える。産卵前の期間に開始し、15日間隔で繰り返します。糖蜜の代わりに10mlのメチルオイゲノールを加えることもお勧めします。
- 48 + _ 10Cで60分間の果実の熱水処理。
- 収穫の3週間前に デルタメトリン2.8EC @ 0.5 ml / l +アザジラクチン(3000 ppm)または2 ml / lをスプレーします。
- ショウジョウバエを防除するためにコバルト60を使用した400G線の果実の照射。
- 蔓延が激しい場合は、 トランクにのみ餌のスプラッシュ、 週に1〜2回の間隔をお勧めします。餌のスプラッシュを準備するには、 1リットルの水に100グラムのジャガリーを混ぜ、古いほうきを使って1mlのデルタメトリンを加えます。
- ショウジョウバエの管理はまた、炭疽病を減らし、晩期の果実の落下を防ぎます。
リーフウェバー

症状:最初、毛虫は解体によって葉の表面を集合的に食べます/後でそれらは柔らかい芽と葉の網を作り、一緒に食べます。いくつかの毛虫は、葉の単一の水かきのあるクラスターに見られることがあります。
管理
- 過密で重なり合う枝の剪定。
- リーフウェブ除去装置による感染したウェブの機械的除去およびそれらの燃焼。
- コナカイガラムシの防除のために以前に行われた果樹園の耕作は、その個体数をチェックします。
- 7月の最後の週から開始する2〜3回のスプレーで、カルバリル(0.2%)またはキナルフォス(0.05%)を使用します。このスパイは、マンゴーpsylla(Apsylla cistellata)の世話もします。
- すべてのスプレーに同じ化学薬品を使用することは避けてください。
ゴールサイラを撃つ
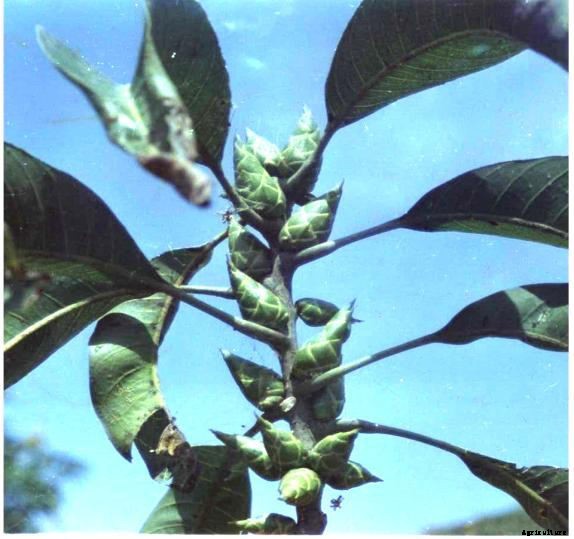

症状:ニンフは8月9月に出現し、隣接する芽から細胞液を吸います。給餌の結果、 つぼみは硬い円錐形の緑色のこぶに発達します。こぶは通常9月から10月に見られます。その結果、開花や結実はありません。ニンフはガリア人の中で冬を過ごします。
管理
- ニンフのいるギャルは集めて破壊する必要があります。
- 8月から隔週でジメトエート(0.06%)またはキナルフォス(0.05%)をスプレーします。
- スプレー2、 4-D(150 ppm、 虫こぶとニンフが出てきて風邪で殺される10月の間に150mg /リットルの水)。
- 湿度の高い地域の新しいマンゴー果樹園は落胆する必要があります。
ステムボーラー

症状:損傷は、根または茎のいずれかの幼虫によって引き起こされます。卵から孵化した後の幼虫は、最初に樹皮を食べ、不規則な虫歯を作ります。それは上向きに退屈かもしれないトンネルを作ります、 枝の乾燥をもたらします
管理
- 果樹園を清潔で健康に保ちます。
- 影響を受けた枝を幼虫と蛹で切って破壊します。
- 穴をきれいにし、ジクロルボス(0.05%)または灯油またはガソリンのエマルジョンに浸した脱脂綿を各穴に挿入し、泥で塞ぎます。
- 緑の硬化病菌の使用、 MetarhiziumanisopliaeまたはBeauveriabassianna。
シュートボーラー
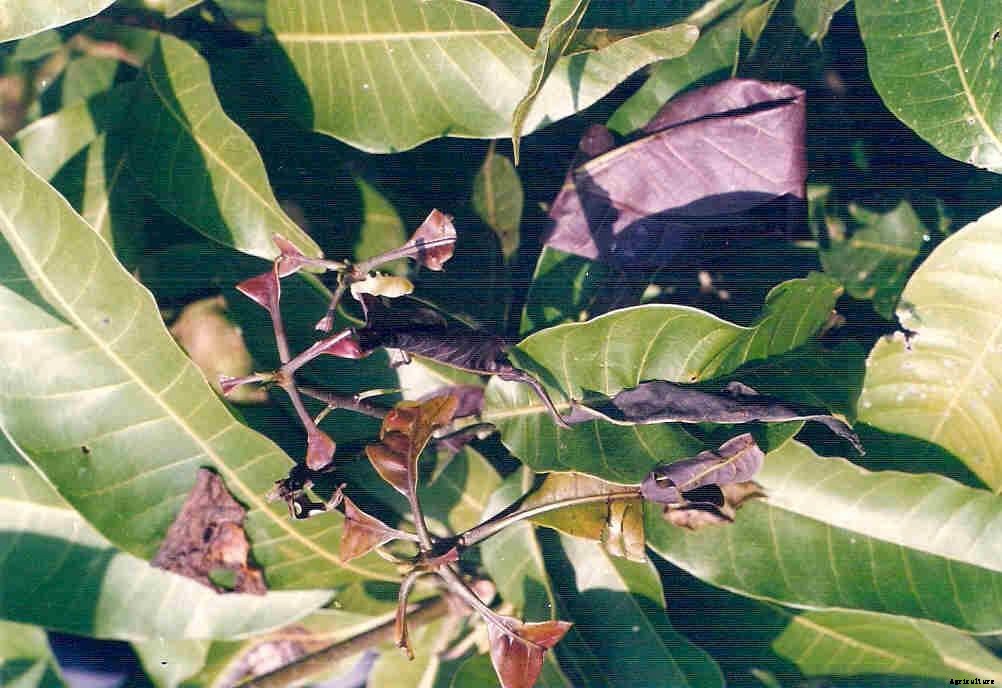

症状:幼虫は8月に若い柔らかい葉に穴をあけ、孵化したての毛虫は中央の肋骨に穴をあけました。数日後、 彼らは下向きにトンネルを掘る成長点の近くで柔らかい芽に退屈しました、 排泄物を投げると、葉が落ち、末端の芽がしおれます。
管理
- 攻撃されたシュートは切り取って破壊する必要があります。
- 新しいフラッシュの開始から隔週でカバリルまたはキナルフォス(0.05%)をスプレーします。
樹皮を食べる毛虫
症状:毛虫は、その排泄物と木の粒子からなる木の上で茶色のジグザグリボンのような絹のウェブを回転させます。幼虫はまた、彼らが休む場所の中に避難所のトンネルを作ります。
管理
- 果樹園を清潔で健康に保ちます。
- 穴をきれいにし、キナルフォスのエマルジョン(0.05%)を各穴に入れ、泥で塞ぎます。
規模
症状:ニンフと成虫の鱗は葉の樹液やその他の柔らかい部分を吸い、植物の活力を低下させます。また、甘露を排出し、葉やその他の柔らかい部分にすすのカビが発生するのを助けます。
管理
- ひどく蔓延している植物の部分を剪定して、樹冠を開き、すぐに破壊します。
- 21日間隔でジメトエート(0.06%)をスプレーします。
- 付随するアリの除去は、天敵が昆虫を制御することを可能にするかもしれません。
アザミウマ:
症状:ニンフと大人は組織を裂傷し、にじみ出る細胞液を吸います。 C.indicusとR.cruentatusは葉を食べ、S。dorsalisは蛍光を発します。 葉の摂食種は葉の先端近くの葉肉を食べます。影響を受けた葉は銀色の光沢を示し、糞便の小さな斑点があります。
管理
蔓延がひどい場合は、 ジメトエート(0.1.5%)またはモノクロトホス(0.1%)のいずれかで制御できます
お茶の蚊のバグ:
症状:カシューナッツの主な害虫、 時々マンゴーや他の果物作物に損害を与えます。成虫は頭が黒い赤褐色の虫で、 赤い胸、 と黒と白の腹部。卵は柔らかい芽の表皮と花序の軸に挿入されます。大人とニンフは葉柄を食べます、 壊死性病変を引き起こす柔らかい芽と葉脈。
管理
ジメトエート(0.05)またはキナルフォス(25 EC)2 ml /リットルをスプレーします。
フルーツボーラー:
症状:オリッサ州の主要な害虫、 西ベンガルと沿岸のアンドラプラデシュ。害虫は1月から5月まで活動します。成虫は果物に卵を産みます。孵化した後、幼虫は実をつけました。完全に成長した毛虫(25 mm)は、体に赤い帯があり、白い帯が交互になっています。毛虫は底(くちばしの領域)で果実に穴をあけ、内部で穀粒に到達します。入口の穴は排泄物で塞がれています。影響を受けた果物は腐敗し、時期尚早に落ちます。
管理
- 果実収穫後の果実と枯れ木の収集。
- 落ちた果物をすべて破壊します。
- 大理石サイズ以降にフェンチオン(0.1%)をスプレーし、重度の感染の場合は2週間後にDeltamethrin 28 EC @ 1ml / lで繰り返します。
- 収穫前の2週間はスプレーをかけないでください。
リーフマイナー:
症状:小さな毛虫が柔らかい葉の背側の流行の下で採掘し、その結果、灰色がかった白い水ぶくれが葉に現れます。
管理
- 切り取られて、影響を受けたシュートを破壊します。
- 新しいフラッシュの出現からキナルフォス(0.05%)またはフェンチオン(0.1%)をスプレーします。
赤い木の蟻
症状:アリは数枚の葉を網で縫い合わせます。 通常、枝の上部にあり、巣を作ります。アリは肉食性で、小さな昆虫を捕食します。しかし、 間接的な被害は、アブラムシや鱗などの昆虫を保護することによって引き起こされます。 蜂蜜の露を排泄します。
管理
- 巣は、ウェブ切断装置によって機械的に除去および破壊する必要があります。
- 接触殺虫剤を噴霧し、 巣を乱した後、1.5ml / lのジメトエート。
花序の毛虫
症状:毛虫は花序を攻撃し、制御されていない場合、結実が減少することで大きな損失を引き起こします。
管理
効率的な管理のために、初期の穂の出現時にモノクロトホスまたはジメトエート1ml / lをスプレーします。
シロアリ

症状:シロアリは白色で、 恥ずかしがり屋で、地下に留まります。彼らは根を食べたり、上に移動してトンネルを作ります。彼らは木の幹の上に、そしてこれらのギャラリーの保護の下で泥ギャラリーを建設します。彼らは幹の樹皮を食べます。
管理
トランクのマッドギャラリーを取り外し、トランクにマラチオン(1.5 ml / l)を拭くかスプレーします。
2か月後、 木の根元の土をクロルピリホス1.5ml / lで浸します。
病気
うどんこ病
症状:病原体が花序を攻撃し、 葉っぱ、 花序と若い果実の茎と真菌の白い表面的な粉状の成長がその脱落をもたらします。がく片は花びらよりも比較的影響を受けやすいです。影響を受けた花は開くことができず、時期尚早に落ちる可能性があります(図28)。未受精の感染した花を落とすと、深刻な作物の損失につながります。最初は若い果物は完全にカビに覆われています。果物がさらに成長すると、 感染した果実の表皮にひび割れやコルク組織が形成されます。果物は、大理石のサイズに達するまで木に残り、その後、時期尚早に落ちることがあります。
肩の壊死性病変
茎の端の葉の下面にカビがあり、そこから落ちる
若い葉に感染が見られますが、 色が茶色から薄緑色に変わったとき。 Young leaves are attacked on both the sides but it is more conspicuous on the grower surface. Often these patches coalesce and occupy larger areas turning into purplish brown in colour. The pathogen is restricted to the area of the central and lateral veins of the infected leaf and often twists, curl and get distorted.
Reason for severity
- 高湿度、 cludy weather &high wind velocity for 3-4 day.
- Minimum temperature (10-130 C), maximum 27-31 0 C and RH 82-91% are most conducive for disease severity.
- Third and fourth week of March attains maximum severity in UP plains.
- Lack of timely fungicidal Schedule.
- Close planting without canopy management.
Mode of Spread
- Spread is dependent on development of mildew pathogen persist on older leaves/ malformed panicles during off season.
- Disease spread through wind borne spores released between 1100 to 1600 hour, which takes 5-7 hours for infection after germination.
管理
- Prune diseased leaves and malformed panicles harbouring the pathogen to reduce primary inoculum load.
- Spray wettable sulphur (0.2%) when panicles are 3-4 in size.
- Spray dinocap (0.1%) 15-20 days after first spray.
- Spray tridemorph (0.1%) 15-20 days after second spray.
- Spraying at full bloom needs to be avoided.
炭疽病
Symptoms:The pathogen causes leaf spot/leaf blight, wither tip, blossom blight and fruit rots. On leaves characteristic symptoms appear as oval or irregular vinaceous brown to deep brown spots of various sizes scattered all over the leaf surface. Later lesions get blighted and rupture and show, shot hole symptom
Blossom blight phase
Typical Anthracnose on cultivar
Young leaves are more prone to attack, than older ones. Petiole, when affected, turns grey or black. Disease also produces elongated black necrotic areas on twigs. The tips of young branches start drying from tip downwards. On blossom small black spots appear on panicles and open flowers, which gradually enlarge and coalesce to cause death of flowers. The infected flowers fall-off, leaving more persistent spikes on peduncles.On fruits, it is more common during transit and storage
Reason for severity
- Closer spacing for not doing pruning
- Due to lack of regular spraying against the disease
- Due to negligence of orchard hygene.
Mode of Spread:
- Disease spread by rain splash, spores infect all above healthy tissues on the host.
- Fungus also produces spores on dead twigs, leaves inflorescence and fruits which further make the disease more complex.
- Free moisture available in the orchard enhances disease spread.
- Pathogen remained viable for 14 months on fallen leaves, dead stem and diseased twigs attached to trees.
- Temperature , 25-30 95%;Relative &humidity for 12 hours is conducive for development of disease.
- Movement of planting material / fruits containing infected foliage / fruits..
管理
- Diseased leaves, 小枝、 gall midge infected leaves and fruits, should be collected and burnt.
- Blossom infection can be controlled effectively by spraying of Bavistin (0.1%) at 15 days interval.
- The foliar infection can be controlled by spraying of copper oxychloride (0.3%)
- Pre-harvest sprays of hexaconazole (0.01%) or Carbendazim (0.1%) at 15 days interval should be done in such a way that the last spray falls 15 days prior to harvest.
- Hot water treatment at 520, 10C for 20 minutes. The duration can be reduced to 10 minutes by supplementing Carbendazim or prochloraz both (0.05%) in hot water.
- Covering the fruits on tree, 15 days prior to harvest with news or brown paper bags.
- Use bio control agent viz Streptosporangium pseudovulgare 。
Die back
Symptoms:The pathogen causing dieback, tip dieback, graft union blight, twig blight, seedling rot, wood stain, stem-end rot, black root rot, 果物の腐敗、 dry rot, brown rot of panicle etc. The disease is most conspicuous during October November. It is characterized by drying back of twigs from top downwards, particularly in older trees followed by drying of leaves which gives an appearance of fire scorch (Fig.36 &Fig. 38). Internal browning in wood tissue is observed when it is slit open along with the long axis. Cracks appear on branches and gum exudes before they die out. When graft union of nursery plant is affected, it usually dies.
Mode of spread
- By planting material containing diseased foliage.
- Disease twigs bearing fruiting bodies are the main source for perpetuation andspread for the next season.
- By using infected budsticks to new areas.
- By inoculums already present in the orchard
- By contaminated garden tools.
Reason for Severity
- Lack of timely control of stem borer which helps in making the tree more prone to disease development.
- Lack of proper cultural operation, つまり。 pruning of disease twig and application of paste around tree trunk.
- Due to lack of application of copper around the tree trunk in sandy soil.
- Tree damaged by gummosis, 昆虫、 drought and lack of nutrition favour the disease development.
- High summer temperature predispose the plant to the attack of pathogen through reducing the vitality of the plant.
Spread of disease
- By planting material containing disease on stem/leaves.
- Disease twigs bearing fruiting bodies are the main source for perpetuation and spread for the next season.
- By using infected budsticks to new areas.
- By inoculums already present in the orchard
- By contaminated garden tools.
管理
- Scion wood selected for propagation should be free from infection
- Every care should be taken to prevent introduction of disease in newly planted orchards.
- Any infected portion should immediately be pruned, followed by spraying/ pasting of copper oxychloride(0.3 %) or pasting with cow dung at the cut ends.
- Pruning should be done in such a way that some healthy portion is also removed, to ensure complete eradication of pathogen (3 “below the infection site).
- The affected branches should be collected and burnt.
Sooty Mould
Symptoms:It is very common wherever honey dew secreting insects, つまり。 mango hopper, scales, coccids and mealy bugs are found. Black velvety thin membranous covering on leaves, stems and fruits are its symptoms.重症の場合、 trees appear black and look ugly.
Mode of Spread:
- Disease spreads by insect execrating honey dew or sugary substances.
- Growth of fungus is associated with the infestation of scale insects.
Reason for high severity
- Closer spacing where light penetration is low.
- High humidity flavors the development of honey dew insects and disease development.
- Lack of timely control of honeydew exerting insects
- Disease incidence is associated with insect severity.
管理
- If honey dew secreting insects are controlled by suitable insecticides, the mould dies out for want of a suitable growth medium. Spraying of monocrotophos (0.05%) at 10-15 days intervals is quite effective.
- Spraying of starch @2% is effective.
- Spray wettable sulphur +monocrotophos +gum acacia (0.2+0.05+0.3%) or Indian oil formulation No. 1 , 2 (4%) at 15 days interval.
- Application of pesticides should cover both sides of leaf.
Phoma blight
Symptoms:The disease is noticed on matured / old leaves only. Fully developed spots are characterized by dark margin and dull grey necrotic centre.重症の場合、 spots coalesce to form patches, which result in withering and defoliation of infected leaves .
管理
- Spray copper oxychloride (0.3%).
- Balanced nutrition provides resistance to phoma blight.
Bacterial canker disease
Symptoms:The disease is noticed on leaves, 葉の茎、 茎、 小枝、 branches and fruits, initially producing water soaked lesions, later turning into typical canker. On leaves, water soaked irregular satellite to angular raised lesions measuring 1-4 mm in diameter are formed. These lesions are light yellow in colour, initially with yellow halo but with age enlarge or coalesce to form irregular necrotic cankerous patches with dark brown colour.
Infection on Leaf Stalks
On fruits, water-soaked, dark brown to black coloured lesions are observed which gradually developed into cankerous, raised or flat spots. These spots grow bigger usually up to 1 to 5 mm in diameter, which covers / almost the whole fruit. These spots often, burst extruding gummy substances containing highly contagious bacterial cells.
Mode of spread:
- Long distance spread is through planting material and infected mango stones.
- In orchard, wind splashed rains
- By collateral host (Weeds), and high wind velocity favours the spread of disease
- Infection is enhance when rains occur in concert with wind which promote wounding of leaf surface.
Reason for high severity:
- Growing of susceptible varieties in and around orchard
- Disease development is favoured by high humidity (90% RH), moderate temperatures (25-300 C ), high wind velocity is congenial for severity of disease
- Lack of wind breaks to reduce wounding and removal of symptomatic portion of trees to reduce inoculums in the orchard.
- Lack of removal of collateral hosts in the area.
管理
- Regular inspection orchards sanitation seedling certification are recommended as preventive measures.
- Mango stones for raising seedlings (root stock) should always be taken from healthy fruits.
- Use wind-breaks helps in reducing brushing/ wounding and thus reduces chance of infection.
- Three sprays of Streptocycline (200ppm) at 10 days intervals reduce fruit infection.
- In severe infection, spraying of Streptocycline (300 ppm) or copper oxychloride (0.3%) is more effective.
- An antagonistic phytoplane bacterium, Bacillus coagulans 、 is found effective.
Malformation

Symptoms:Vegetative malformation is pronounced in young seedlings. The affected seedlings develop vegetative growths which are abnormal growth, swollen and have very short internodes.
Floral malformation:The flower buds are transformed into vegetative buds and a large number of small leaves and stems, which are characterized by appreciably reduced internodes and give an appearance of witches broom. The flower buds seldom open and remain dull green.
管理
- The floral malformed panicles/ vegetative malformed shoots should be pruned and burnt which reduces the incidence of malformation.
- Application of NAA (200 ppm) or planofix (90 ml/ 20 l) in the first week of October (Before bud differentiation stages) followed by deblossoming in the late December or January or bud burst stage reduces the incidence of malformation.
- Spray chelated Zn++(100 ppm) and Cu++(40 ppm) during flower bud differentiation and flowering stage combined with spray of carbendazim (0.1%) during November- December.
Gummosis
Symptoms:The disease is characterized by the presence of profuse oozing of gum on the surface of the affected wood, bark of the trunk and also on larger braches but more common on the cracked branches.重症の場合、 droplets of gum trickle down on stem, bark turn dark brown with longitudinal cracks, rots completely and the tree dries up because of cracking, rotting and girdling effects.
管理
- The diseased bark / portion should be removed or cleaned and pasted with Bordeaux paste or copper oxychloride paste or cow dung paste or cow dung paste .
- Application of Copper sulphate 500 gm/ tree (depending upon the age of the tree) in soil around the tree trunk is recommended. Gummosis is very less in the orchards receiving regular copper oxychloride sprays for control of leaf spot diseases.
かさぶた

Symptoms:The scab fungus attack leaves, panicles, blossoms, 小枝、 bark of stems and mango fruits. Spots are circular, slightly angular, 細長い、 2-4 mm in diameter, brown but during rainy season, lesions differ in size, shape and colour. Symptoms produced by the disease are very much like those of anthracnose. On young fruits, the infection is grey to grayish brown with dark irregular margins. As the fruit attains in size, spots also enlarge and the centre may become covered with the crack fissure and corky tissues.
管理
- Frequent sprays of copper oxycholoride (0.3%) to protect new flushes of growth are effective for scab control in nurseries.
Black Banded
Symptoms:The disease is noticed on the midribs/ veins of the leaves, twigs and branches as black velvety raise fungal out growth in the form of spots which gradually increase insize encircle the trunk limbs branches and twigs. The incidence of disease is very low on the main branches. The disease occasionally spread on the leaves and cause loss. It presents a characteristic and conspicuous black banded appearance and thus considered appropriate to name it as Black banded diseases.
管理
- Gunny rubbing on twigs/ branches to remove the black growth.
- Spraying of Bordeaux mixture (5:5:50) or copper oxychloride (0.3%).
Symptoms:The leaves of affected tree area lusterless and sparse. Diseased tree wilts and dies. Infected roots are very light in weight and get easily crumbled and powdered with fingers. The fruiting bodies of the fungus (brackets) appear at the base of the tree in rainy season.
Root Rot Damping off

Symptoms:The disease is characterized by sudden dropping of leaves after the emergence of seedlings from the soil. During prolonged rainy and humid weather, infection occurs at / or below the ground level with circular to irregular water soaked patches. These patches enlarge and ultimately girdle the entire base of the seedlings.
管理
- Care should be taken that water should not stagnate near the root zone.
- Nursery should be raised on elevated beds.
- Nursery beds should be fumigated before sowing.
- Application of Trichoderma in the affected nursery is effective.
- 成長期には、 Bordeaux mixture (1.5%) should be sprayed on the plants and the soil at weekly intervals.
Red rust
Symptoms:The disease is readily recognized by the presence of the rusty red fructification of the alga on the surface of the leaves, veins, petiole and young twigs and fruit. Initially the spots are greenish grey in colour and velvety in texture which finally turn into reddish brown in colour.
管理
- If vigour of plant is maintained by balanced nutrients, the disease is less.
- Spray Bordeaux mixture (5:5:50) or copper oxychloride (0.3%).
- As the disease starts on the onset of rain, it is desired to spray fungicide twice during the month of July/ August at 15 days intervals.
Lichens
Symptoms:Lichens are found on full grown trees of mango, mainly on trunks, branches and twigs in the areas of high humidity, heavy rainfall and poorly managed orchards. It is seen in the form of whitish, pinkish, superficial patches of different shapes on the main trunk, 枝、 leaves and twigs of the trees.
管理
- Field sanitation and balanced nutrition help in checking the disease.
- The lichens can be managed by gunny rubbing followed by spraying the trunk, 枝、 twigs with commercial caustic soda (1.0%)
POST HARVEST DISEASE
炭疽病

症状
The post harvest infection starts form the field as latent infection. On stored fruits, black spots are produced. Initially the spots are round but later coalesce to form large irregular blotches.ときどき、 it covers the entire fruits surface. The spots have large deep cracks in which fungus penetrates deep into the fruit, causing extensive rotting. Under moist conditions, the blackened areas become covered with minute pinkish reproductive bodies of the fungus. Staining, russetting and tear streaking, involving only the skin of the fruit, are attributed to the same fungus .
管理
- The major strategies in controlling post harvest anthracnose are scheduled preharvest sprays with thiophanate methyl or carbendazim (Topsin M OR Bavistin 0.1%) in the field to reduce the latent infection and treatment of the fruits with hot water along or hot water with fungicides after harvest to eradicate the left over latent infection.
- Hot water treatment along at 52 + (-) C for 3 minutes gives good control of anthracnose.しかし、 the duration of hot water treatment can be reduced to 15 minutes by supplementing it with fungicides, つまり。 carbendazim or thiophante methyl (Bavistin or Topsin M 0.05%).
Stem end Rot Symptoms

The disease starts on fruit at the base of the pedicel. A circular brown area develops near the stem end, which gradually starts developing as dark brown to black area towards the lower portion of the fruit and later even cover the entire fruit surface. The rotting is so fast that the entire fruit rots within 2-3 days. The disease may start on fruit from some point other than the stem end, when fruit get bruises. The disease is observed on ripe fruits only.
管理
- Pre harvest sprays of carbendazim or thiophanate methyl (Bavistin or Topsin M 0.1%) 15 days before harvesting control the post harvest rot due to stem end rot.
- As the disease starts from the stem end, it is desired that the harvesting along with 5 cm stalk, the disease is checked. If fruits are harvested without stalk, the opening should be closed with wax.
- Disease can be controlled by dipping the fruits in hot water 52 C with 0.05% cabendazim for five minutes.
黒腐病
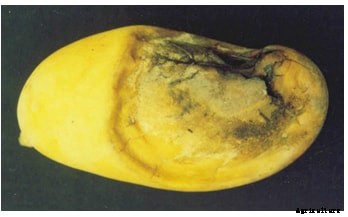
症状
Affected fruits show characteristic yellowing with irregular dull grayish spots, which develop into the black necrotic area with growth of black mould. Tissue below and around the spots disintegrate and emit foul dour. The fruits rot very fast. The rotting may; start from any point but injury is essential for the start of rot. It may also start form the stem end as there remains natural opening.
管理
- It is desired that the harvesting of fruits is done carefully as any injury to fruit predisposes it to the attack of Aspergillus rot.
- Fruits should not be allowed to touch soil.
- Fruit harvesting and handling should be done carefully in clean manner.
- Diseases can be controlled by dipping fruits in hot water 5210 C with 0.05% cabendazim for five minutes.
USEFUL TIPS FOR MINIMIZING POST HARVEST DISEASES
- Start controlling post harvest diseases before harvest.
Reason:Many post harvest diseases begin while the crop is still in the field. Some harvested fruits carry latent infection that may not be detected at harvest level.
- Avoid injuring the commodity throughout the entire distribution process from harvesting to marketing.
Reason:Bruises, wounds and other mechanical injuries serve as portal of entry for microorganisms.
- Clean the commodity of soil and other sources of infection after harvest.
Reason:These may carry the microorganisms from the field.
- Keep the fruits dry after washing.
Reason:Free moisture on the fruits surface enhances the growth of spores.
- Separate ripe from unripe fruits either in the containers or storage rooms. Reason:Ripefruits serve source of inoculums (decay-causing microorganisms).
- Handle the fruits carefully during harvesting, sorting, packaging and storing.Reason:Careless handling may bruise the fruits, thus, providing entry points for disease-causing microorganisms.
- Separate diseased commodities from healthy ones.
Reason:Diseased commodities may contaminate healthy fruit when they come in contact with diseased ones.
- Store commodities at the recommended temperature.
Reason:Disease-causing microorganisms do not grow at low temperatures. Growth will resume upon transfer of commodity to room temperature.
- Provide aeration in storage areas and keep the commodity free of excess moisture.
Reason:Moist conditions favour the growth and multiplication of disease- causing microorganisms.
- Practice sanitation and cleanliness at all times in transit, storage areas, containers and market stalls.
Reason:Dirty and unsanitary containers and areas may serve as sources of infection.
Black Tip

Symptoms:Symptoms become visible when the mango fruits attain some size. Small etiolated area develops near the distal end of the fruit which gradually spreads, turns nearly black and covers the tip of the fruit completely. The black area remains hard and the growth of the fruit is checked.
Black Tip on cultivar Dushehri Reason for high severity:
- Proximity of orchard-to brick kilns.
- Deleterious effect of gases from brick kilns operating in the vicinity of orchard.
- Wind direction (western winds) and velocity play important role in severity
- Lack of timely control measures.
Mode of Spread
Through toxic gas viz. Sulphurdioxide, ethylene, carbonmonooxide and fluoride emitting from brick klins operating nearby orchard.
管理
- It can be can be minimized by the spray of borax (1%) or other alkaline solution like caustic soda and washing soda. The first spray should be done positively at pea stage followed by two more sprays at 15 days interval.
- Planting of mango orchard in north-south direction and 3 km away from the brick kilns reduce the incidence.
Internal Necrosis (Boron deficiency)
Symptoms:First, water soaked grayish spots develop on the lower side of the fruit. Late, the spots enlarge and develop into dark brown necrotic area. The internal tissue starts disintegrating. The pericarp and mesocarp is disintegrated exposing the flesh.
Yellow coloured droplets also come out and such affected fruits drop easily.
Internal Necrosis on hanging fruits and close up Management
- Foliar spay of borax (1%) at pea stage followed by two more sprays at 15 days interval.
- Application of 250 gm boron per tree (10-15 year old) around the tree basin.
Fruit Clustering

Symptoms:This abnormality is characterized by formation of several fruit lets at the tip of panicle. The fruitlets are darker green in colour and their shape is slightly curved than the normal fruits. These fruits generally hang for more time compared to some normal fruits, which subsequently drop due to other fruit drop reasons. However these fruitless do not grow more and later drop. The fruits do not have formation of seeds.
管理
- During flower opening or pollination stages spray of insecticides and fungicides should be avoided.
- Population of pollinators should be kept more during flowering season.
- Pollinizing cultivars should be planted in the orchard.
- Increase pollinator population by keeping bee hives in the orchards.
Woody Stem gall

Symptoms:Woody galls of 10-15 inches diameter are formed on limbs and branches. The galls are abundant on CVS. Chinnasuvarnarekha, Langra and moderate in Neelam.
管理
- Remedy lies in removal of galls using saw and applying Bordeaux paste to cut surface.
Red nose / soft nose (Cause not known)

Symptoms:The malady is severe in late maturing Neelam and Mallika varieties particularly in delayed harvest leading to substantial loss. The fruits with red nose are unfit for export. Numerous red nosed fruits are seen on tree during fag end of summer with onset of showers. Red nose gradually becomes soft and rot.
管理
- Timely harvesting of fruit.
- Proper nutrition to the plant.
Fruit tumors
Symptoms:Tumors of pea to marble size develop on fruit and are very ugly to look at. The stylar end part is much affected while stem end is practically free from tumors
Fruit showing tumors Management
- Removal of affected fruits from the tree and buried in the soil.
Softening of tissue
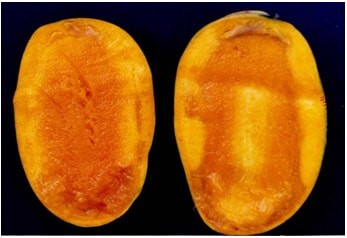
The problem of jelly seed have been recorded in several mango varieties.しかし、 Dashehari cultivar of mango is found more susceptible to this disorder as compared to other cultivars like Chausa and Langra. In this disorder, the pulp near the stone becomes jelly like with tissue disintegration while the outer pulp near the peel is normal. The taste of fruit becomes repulsive and loose table quality. From the outer appearance fruits look normal. It incidence is more in Lucknow region particularly in late harvested fruits (Fig. 74).
Most of the prone orchards of this disorder have been found with imbalance of nutrients. Among the nutrients, P and Zn deficiency were more prevalent. Slow movement of nutrients particularly Ca++ to the fruits from soil and leaf through transpiration stream in Dashehari at maturity was found to be one of the reasons for this disorder.
管理
- An integrated approach is found effective for the control the softening of tissue. This includes application of black plastic mulch (100 u thick) in the basin of tree during the month of October- November and foliar spray of calcium chloride dehydrate (2.%) and potassium sulphate (1%), one month before harvesting of fruits along with application of 250 g Borax per tree in soil during the month of November.
- It is desirable to harvest fruits at proper maturity (not late) and make it to ripe in storage rather than to allow on plants.
Spongy tissue
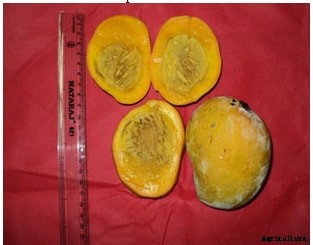
Alphonso mango, which is the main export cultivar, suffers from a serious malady known as spongy tissue or internal breakdown in the ripe fruits. This disorder renders the fruit unfit for consumption and hence, it has become a bottleneck in export and expansion of its cultivation in the State of Maharashtra and Gujarat where it is grown commercially. There are many biochemical changes associate with spongy tissue;しかし、 no conclusive results have been obtained to control this malady. Convicting heat arising from soil and intense solar radiation are reported to be the main cause for this disorder.
管理
- Mulching with paddy straw and dry leaves was found effective for its control.
NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS
Potassium deficiency
Symptoms:Scorching of leaf margins is the characteristic symptom of potassium deficiency. Scorching starts from tip downwards. Fruit quality is reduced. Trees with potassium deficiency are easily prone to pest and disease attack.
Scorched Leaf Margin
管理
- Application of 1 kg muriate of potash or sulphate of potash along with 2 kg urea and 6 kg super phosphate during July-August in the basin could rectify potassium deficiency.
- Dropped leaves should also be incorporated along with manures to enrich the soil health and fertility.
Zinc deficiency

Symptoms:The leaves become small and narrow with leaf margins bent upward or downward. Inter nodal length is reduced drastically and the twig with crowded leaves gives rosette appearance. Pale inferential areas and green veins are typical of zinc deficient leaves. The tree with zinc hunger does not grow well and the yield, size and quality of the fruit are reduced. Small plants with severe zinc deficiency may die. Zinc deficiency is conspicuously seen in alkaline, saline and sandy soils.
Deficiency Symptoms of Zinc
管理
- Zinc deficiency can be rectified by spraying of zinc sulphate 5 g +10g urea /1 water twice at 15 days interval.
Iron deficiency
Symptoms:The leaves loose green colour and turn white and is called Bleaching. The size of the leaf is reduced. In severe cases of iron deficiency, the leaves dry from tip downwards. The deficiency is common in soils with high calcium content.したがって、 the effect is known as calcium induced iron chlorosis.
管理
- Two sprays at fortnight interval with ferrous sulphate 2.5 g per liter.
Boron deficiency
Symptoms:Cracking of fruit is the characteristic symptom of boron deficiency. Lusterless leathery leaves with thickened veins are the other associated symptoms. Brown areas in yellow fruit pulp are conspicuous.
管理
- Application of 250gm boron per tree (10-15 year old) with recommended dose of manures during July-August.
Salt injury / Toxicity

Symptoms:The leaves are scorched due to excess salt in soil or irrigation water. The leaves lose their natural colour and turn to bronze colour. Tip burning is also seen in severe cases of salt injury.
Management:
- Raise Dhiancha as green manure crop with onset of monsoon in the inter-spaces of the orchard during tree bearing years and remove.
- Farm yard manure and compost should be applied adequately every year.
- Gypsum filled gunny bag if kept in flowing irrigation water will reduce salt effect.
銅欠乏症
Symptoms:Copper deficiency symptoms frequently develop on young trees which generally occur due to heavy nitrogenous fertilization. It may also be accompanied by Zinc deficiency symptoms. The appearance of weak terminal shoots followed by defoliation and die back of branches, on the top of long drooping or shaped branches of the proceeding cycle of growth usually makes evident that copper is needed
管理
- Application / spraying of Copper (250 g/ 10 years tree) or Copper oxychloride (0.3%) at monthly interval.
PEST MONITORING
Survey:To monitor the initial development of pest and disease in the endemic areas survey is prerequisite.したがって、 for field scouting farmers should be mobilized to observe the pest and disease occurrence at the intervals as stipulated under different development stages. The plant protection measures are required to be taken only when bio control potential does not show promise and pest and disease incidences shows increasing trend.
Field Scouting:Field scouting for pests/disease and bio control fauna/flora by extension agencies and farmers once in a fortnight should be undertaken to assess increasing/decreasing trend in the pest/disease incidence and availability of bio control potential. This should be done soon after the appearance of new flush after the fall of old leaves as such stage of the crop having succulent tissues in valuable to attack by pests and diseases. The state Departments of Horticulture should make all possible efforts by using different media, mode and publicity to inform the farmers for field scouting in the specific crop area having indication of pest and disease build up.
Pest Monitoring through Traps:
- Through yellow sticky traps:Setup yellow fast coloured sticky traps for monitoring sucking pests one trap/5 trees. Locally available empty yellow Palmolive-tins coated with grease/ Vaseline/castor oil on outer surface may also be used.
- Sex pheromone traps:These traps are very useful tool in monitoring and control of population of fruit fly. Hanging of traps containing 100 ml of water emulsion of methyl eugenol (0.1%) + malathion (0.1%) during fruiting season (April-July) is very effective for control of fruit fly. Ten traps per hectare of orchard gives satisfactory control. Traps can be fixed during morning hours.
IPM STRATEGIES
Cultural Practices
- Deep ploughing of orchard immediately after harvest to expose eggs and pupae of mealy bug, inflorescence midge and fruit fly.
- Heavy irrigation of orchard in October also helps in destruction of eggs of mealy bug, diapause pupae of midge and fruit fly.
- Avoid dense planting, keep orchard clean by regular ploughing, removal or weeds and prune the over crowded and overlapping branches in December for control of hoppers.
- Raking of soil around the tree trunks and mixing with methyl parathion 2% dust
- 250 g per tree for controlling early instars nymphs of mealy bugs in t he month of November-December.
- Collection and destruction of stone weevil infested fallen fruits and stones help in reduction and carry over of infestation.
Mechanical Control
- After mud plastering 25 cm wide, 400 gauge alkathene (Polythene) sheet should be fastened to the tree \trunk with the help of sutili, about 30 cm above the ground level to prevent migration of freshly hatched first instar nymphs of mealy bugs in the month of November-December.
- Early harvesting of mature fruits to avoid fruitfly infestation, collection and destruction of fruit fly infested fruits.
- Removal of webs made by leaf webber by leaf removing device and burning them in August to September to control leaf webber.
- Pruning of overcrowded and overlapping branches for control of leaf webber dried portion and pasting of copper oxychloride for control of dieback disease.
- Diseased foliage / twig infected with anthracnose disease should be pruned during these months.
- Removal of powdery mildew infected leaves and malformed panicles in April.
Biological Control
A large number of parasites, predator and pathogens are very active against pests of mango in the fields.これらは Rodolia fumida, Suminus renardi, Coccinellids, Beauveria bassiana, Verticillium lacani, Mallada boninensis, Chrysopa spp., Tertrastichus spp., Trichoderma spp., Gonatocerus spp, Podynema spp., Platygaster sp, Eupulmus sp., Systasis dasynearue, Micronimus timidis, Baccha pulchrifrons, NS 。 which pay a significant role in population suppression of various insect pests and diseases. These should be conserved in the field.
Chemical Control
Chemical pesticides recommended for control of diseases and pests are given in the text.
SOME USEFUL TIPS IN PEST MANGEMENT
- Always use protective clothing while spraying.
- Avoid spraying insecticides repeatedly. Alternate them with botanicals, wherever possible to prevent development of resistance and pest resurgence.
- Add 0.5 ml of any sticking agent to the spray solution.
- Oil should be made into an emulsion before spray by shaking thoroughly in a bottle before dilution and sprayed immediately without any delay.
- Botanicals may cause phytoxicity when the temperature is more than 32 0 C in polyhouse. Hence it should be done with caution and only after pre-checking.It is always better to spray botanicals in the evening.
- After spraying any insecticide keep appropriate waiting period before harvesting fruits.
- Preparation of neem seed powder extract 4%:Soak 4 kg of pulverized neem seed powder in 20 litres of water overnight or 12 ha. Thereafter, filter through a fine cloth or double layered nylon net and make to 100 litres and spray. One hectare of the crop requires 1000 litres of spray fluid and 40 kg of neem seed powder.
- Preparation of oil emulsion for spray:When oil is used either alone or mixed with insecticides, the spray fluid should be made into an emulsion. Take required quantity of oil in a plastic bottle, add sticker and required quantity of insecticide (if oil has to be mixed with insecticide), double the quantity of oil, shake thoroughly, transfer to spray tank, dilute with required water and spray immediately.






























